Broward Community College Antimicrobial Resistance Discussion
I’m working on a microbiology discussion question and need an explanation and answer to help me learn.
The principle of chemotherapy is it can damage the genes inside the nucleus of cells. Some drugs damage cells at the point of splitting. Some damage the cells while they’re making copies of all their genes before they split. Chemotherapy is much less likely to damage cells that are at rest, such as most normal cells. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a natural phenomenon whereby bacteria evolve in such a way to withstand the action of drugs, making them apparently ineffective. The pressure that antimicrobials put on the pathogens is responsible for the selection of resistant strains. Although AMR is a naturally occurring process, and while in the past decades it was believed to be under control, today it is considered a threat for global health and the expectations for the future are not encouraging. There are three main causes of AMR. The first cause is considered to be the use of antimicrobials, which has strongly increased in the last few decades. The second cause lies in the fact that in most cases, the patients are not able to follow the therapy instructions properly. The third cause is due to the fact that within a given class of antimicrobials, there are very limited numbers of new drugs under development to replace those rendered ineffective by rising drug resistance.
——————————-
Chemotherapy agents are used to treat cancers, leukemia’s and lymphomas. There are over 50 such drugs, which can be used as single agents, or in combination, orally, IV and subcutaneously. Chemotherapy refers to agents whose mechanisms of action cause cell death or prevent cell growth, generally through inhibiting microtubule function, protein function, or DNA synthesis. Chemotherapy mechanisms of action may be cell cycle dependent == arresting cancer cell growth at specific phases in the cell cycle. The cell cycle comprises of four stages. The cell must progress through these in order to duplicate its chromosomes and divide. These are: G0 –Normal functions G1 phase (Gap 1). During this phase, the cell is growing and preparing to double its DNA. S phase (DNA synthesis). This is the phase in which the amount of DNA is doubled. G2 phase (Gap 2). The cell prepares for mitosis. M phase (mitosis). Division of the nucleus. The main mechanisms of resistance are: limiting uptake of a drug, modification of a drug target, inactivation of a drug, and active efflux of a drug. These mechanisms may be native to the microorganisms, or acquired from other microorganisms. here are many ways that drug-resistant infections can be prevented: immunization, safe food preparation, handwashing, and using antibiotics as directed and only when necessary.
———————————
Pathogenicity refers to the ability of an organism to harm the host thus causing disease. An organism such as bacteria may cause harm to the host when the bacteria produce toxins or enzymes that will infiltrate and destroy the host cell. A way in which this is done is bacteria multiplying so rapidly that they crowd out the host tissues and disrupt normal function. This can also kill cells and tissues outright as well as make toxins that can paralyze, destroy cells metabolic machinery, or precipitate a massive immune reaction that is itself toxic. The diagram below illustrate how microorganism attack the body.
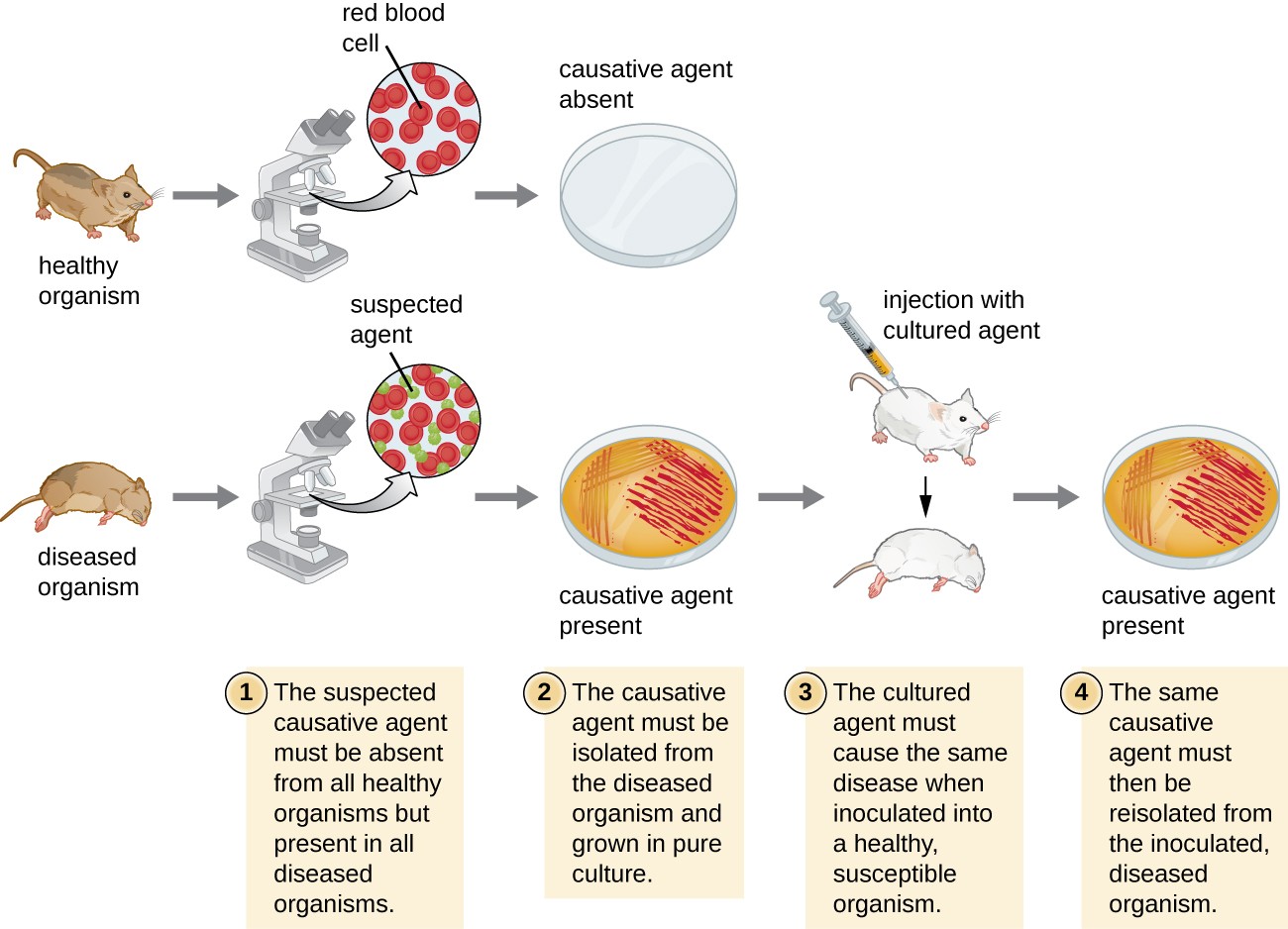
————–
Pathogenesis refers both to the mechanism of infection and to the mechanism by which disease develops. The common pathogenic mechanisms by which microorganisms can attack the body include: Bacterial Infectivity, Host Resistance, Genetic and Molecular Basis for Virulence, Host-Mediated Pathogenesis, and Intracellular Growth. Infection is the invasion of the host by microorganisms, which then multiply in close association with the host’s tissues. Infection is distinguished from disease, a morbid process that does not necessarily involve infection (diabetes, for example, is a disease with no known causative agent). Bacteria can cause a multitude of different infections, ranging in severity from inapparent to fulminating. Virulence is the measure of the pathogenicity of an organism. The degree of virulence is related directly to the ability of the organism to cause disease despite host resistance mechanisms; it is affected by numerous variables such as the number of infecting bacteria, route of entry into the body, specific and nonspecific host defense mechanisms, and virulence factors of the bacterium. Virulence can be measured experimentally by determining the number of bacteria required to cause animal death, illness, or lesions in a defined period after the bacteria are administered by a designated route.
————-
Morbidity is any condition that isn’t healthy. It can refer to mental or physical illness. A person with high morbidity may not live as long as someone who is healthy. However, morbidity doesn’t always mean you are in danger of dying right away. If an illness gets worse over time, it could raise your risk of mortality. Mortality usually means the number of deaths caused by an event or illness over a specific period of time. A mortality rate states the number of deaths as a proportion of a larger group of people. For example, an illness might cause “150 deaths per 100,000 people per year.” Incidence is the number of new cases of diseases, while prevalence is the total number of existing cases of diseases. At their most basic, prevalence describes the here and now, while incidence can be used to try to predict what will likely occur.
————
There is a big difference with the terms morbidity and mortality. Mortality basically means death; Morbidity means to suffer from disease or medical condition. If someone is dealing with morbidity, it might lead to mortality.
Incidence and prevalence have different meanings but are related to each other. Incidence is the number of new cases of a condition, symptom, or death that developed during a specific time period. Prevalence of disease is the total number of people in a population who have a disease or health condition. For example, the incidence of Corona virus this year is different from the prevalence of the disease, which is the total number of cases.
Don't hesitate - Save time and Excel
Are you overwhelmed by an intense schedule and facing difficulties completing this assignment? We at GrandHomework know how to assist students in the most effective and cheap way possible. To be sure of this, place an order and enjoy the best grades that you deserve!
Post Homework